PowerBI and its use in performance management reporting
Monthly reporting utilising Excel dashboards proved to be time consuming, require numerous efforts to provide consistent presentation and was not readily providing the detailed information required to enable prompt effective decisions to be taken by the relevant management teams.
With the switch to PowerBI, significant benefits were achieved in terms of time savings, consistent presentation, and a more immediate response with regards to further level of detail if required due to the interactive nature of the dashboard.
The benefits of PowerBI presentations were seen by senior management, as they received up-to-date information at summary level. PowerBI also gave individuals the immediate opportunity to drill down to the next level of detail in the event that a particular metric deserved further investigation.
Programme wide high-level metrics were shared project wide and with HS2 to keep all informed of progress and help motivate and engage individuals to deliver the programme of works.
Delivery teams, individual disciplines (e.g., Health and Safety, Consents, Environment) and the various individuals who were generating the reports and doing the presentations also received benefits. Once PowerBI had been initially constructed, consistent presentation of metrics to summary level and then further investigation of a metric was immediately available to show at the appropriate level for the audience.
This paper will be of interest to future projects and programmes wishing to improve the efficiency of their performance management reporting by utilising PowerBI to obtain the multiple benefits described.
Background and industry context
With large complex projects, monthly reporting is required to enable management to have information to hand, to ensure that correct decisions can be made in a timely manner with regards to facilitating achievement of project deliverables.
This was the challenge faced by the Enabling Works Contractor (EWC) for the southern section of High Speed Two (HS2) phase one, Costain Skanska joint venture (CSjv).
Approach
The EWC undertook an investigation to identify the information required for the monthly report submission in terms of contractual requirement. Consideration was also given as to the information that management teams required at hand to make timely decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
Excel Dashboards
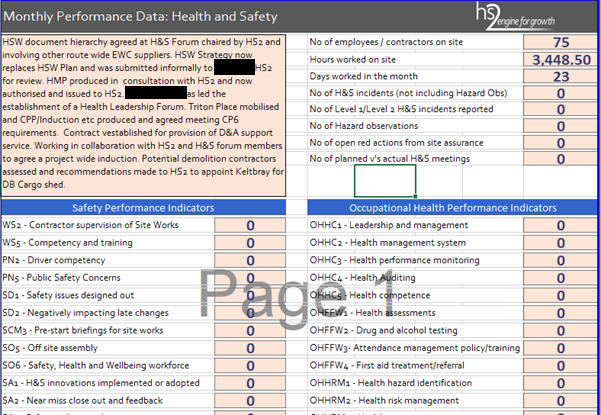
The Excel dashboard (Figure 1) in use had several areas where improvements were identified as being required, as set out below.
- Graphs and charts were found to require additional information to enable decisions to be made. Due to the level of information required, at times more graphs or charts were required to avoid the busy approach on existing graphs. Busy graphs lead to confusion and poor interpretation of information. The requirement for additional information and graphs, led to slower reaction times for decisions.
- Presentation and efficiency – the reports and information being received from the various functions were being returned to Project Controls in different formats or broken formats. Graphs and charts were also required to be re-sized.
- Document size – the Excel reporting dashboard file was circa 120MB, and therefore resulted in additional issues when trying to present the information. Sharing the information or parts of the information with HS2 proved equally challenging.
Switch to Power BI
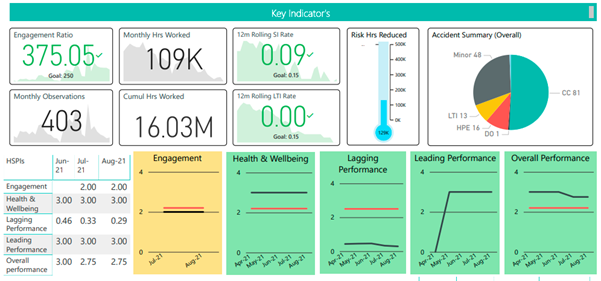
PowerBI provided many distinct advantages over Excel for dashboard reporting the project teams and management:
- PowerBI has interactive charts which can be filtered or grouped. This facilitated the ability to see and provide information at Area, Parcel or Package level as required, rather than having to generate numerous separate graphs to give the same information. Also, PowerBI offers the ability to view time slices as required.
- By utilising PowerBI to provide and show the monthly updated information, time efficiencies were identified. Project Controls did not have to constantly fix broken formatting from the originator. Further time savings were made due to the removal of the need to copy and paste and resize graphs and text.
- Consistent presentation across all functions was easier to maintain for the final output layout, as the layout was controlled by Project Controls in PowerBI. This is because the team was only importing data, whereas previously they would be getting formats changed by the originator, even when they should not have been changing it.
- Another key advantage was the reduction in file size: the size of the Excel reports meant that they were burdensome to handle.
Outcomes and learning
PowerBI has provided significant benefits in terms of time and cost efficiencies, enhanced presentation, and ability to provide time slices. These benefits are seen not only by the functions generating the original reports, but by the teams collating the PowerBI reports through to the various management teams, viewing the reports and undertaking decisions.
PowerBI file size is significantly reduced and easier to handle, making the document easier to share with other key stakeholders and resulting in the same information being used for different communication purposes.
Recommendations
Careful consideration and agreement with key stakeholders is necessary to identify and establish metrics required throughout the phases of future projects and programmes at the beginning of the project. Design metrics will be required at the start of the project, whereas construction metrics can only commence when that phase starts.
This will ensure that appropriate metrics (such as Health and Safety, working at height, or excavations or consents) and information is collated from day one. This will lead to the construction of PowerBI information to best utilise the data and present it in a format that can facilitate the various requirements for different level of reports (i.e., senior management, functions or external stakeholders).
Some metrics will be required for project team and internal stakeholders, while other metrics will be required for the respective Clients and other external stakeholders.
By identifying the metrics at the start, this will in turn lead to a clear understanding of areas generating the information, and ensure that information is obtained in a clear, concise and legible format.
This will facilitate information being available in one place for review throughout the project, and permit the management of key information and retrieval of information as the programme proceeds to its conclusion. In this way, this will also save time on retrieval of key information and facilitate any requests for information.
Conclusion
Using PowerBI reporting rather than the previous Excel reports has proved to be very beneficial and worthwhile. Many efficiencies have been identified in terms of having information readily available in this format.
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Dipak Parshot for his contribution and the Project Controls team for the successful implementation of PowerBI and the continued development to ensure reports are consistently providing the level of information required by management.

