Leveraging Lifetime Cycle Assessment (LCA) for smarter carbon reduction
This article explores HS2’s approach for carbon reduction, emphasising their collaborative partnership with Cerclos in implementing Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology, through the eTool software. HS2 and Cerclos have worked closely to engage stakeholders, improve software to streamline processes and enhance accuracy in LCA results. This strategic partnership offers valuable insights for stakeholders seeking effective methods to integrate an LCA tool into large-scale infrastructure developments.
The approach and key lessons gained are pertinent for future infrastructure projects considering LCA methodology adoption and tool implementation. It is relevant to a diverse array of stakeholders involved in the decarbonisation of the built environment, including architects, asset owners, consultants, contractors, engineers, finance institutions, government entities, property developers, quantity surveyors and sustainability managers.
Background and industry context
In 2019, the UK became the first major economy to mandate net-zero Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions by 2050[1]. Historically, infrastructure and construction industries prioritise cost, schedule, and compliance over environmental performance, despite contributing over half of the UK’s carbon emissions[2]. Reducing these emissions is crucial for national carbon reduction[3] and global climate change mitigation.
The investment in High Speed Two (HS2) was partly justified by its potential to reduce carbon emissions through the high-speed rail network[2]. As a result, HS2’s Environmental Minimum Requirements (EMRs)[4] mandate minimising the program’s carbon footprint with ambitious targets, set to achieve a 50% carbon reduction in the Main Works Civil Contracts (MWCCs)[5] across the design, construction and operation phases of their assets, which include buildings, tunnels, viaducts, cuttings, stations and railway systems. HS2 supports these goals with a carbon management plan that includes a Greenhouse Gas Emissions assessment aligned with international standards BS EN 15978, BS EN 15804, PAS 2080:2016 Carbon management in infrastructure[5], employing Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology which is also widely adopted by major green certification schemes such as BREEAM. Life Cycle Assessment evaluates the environmental impacts of a product, process or service throughout its entire life cycle, considering all stages from raw material extraction, through production, use, and disposal or recycling. The goal of LCA is to provide comprehensive insights to guide decision-making for sustainable outcomes. While LCAs can be applied at any stage of the project, the optimal stage to maximise emissions reduction is in the early design phase – as approximately 70% of impacts are locked in during the first 10% of the design development stage[6].
Thus, integrating a robust LCA process shown in Figure 1 was essential for HS2 to effectively execute its plan, addressing carbon emissions throughout construction and a 120-year operational period.
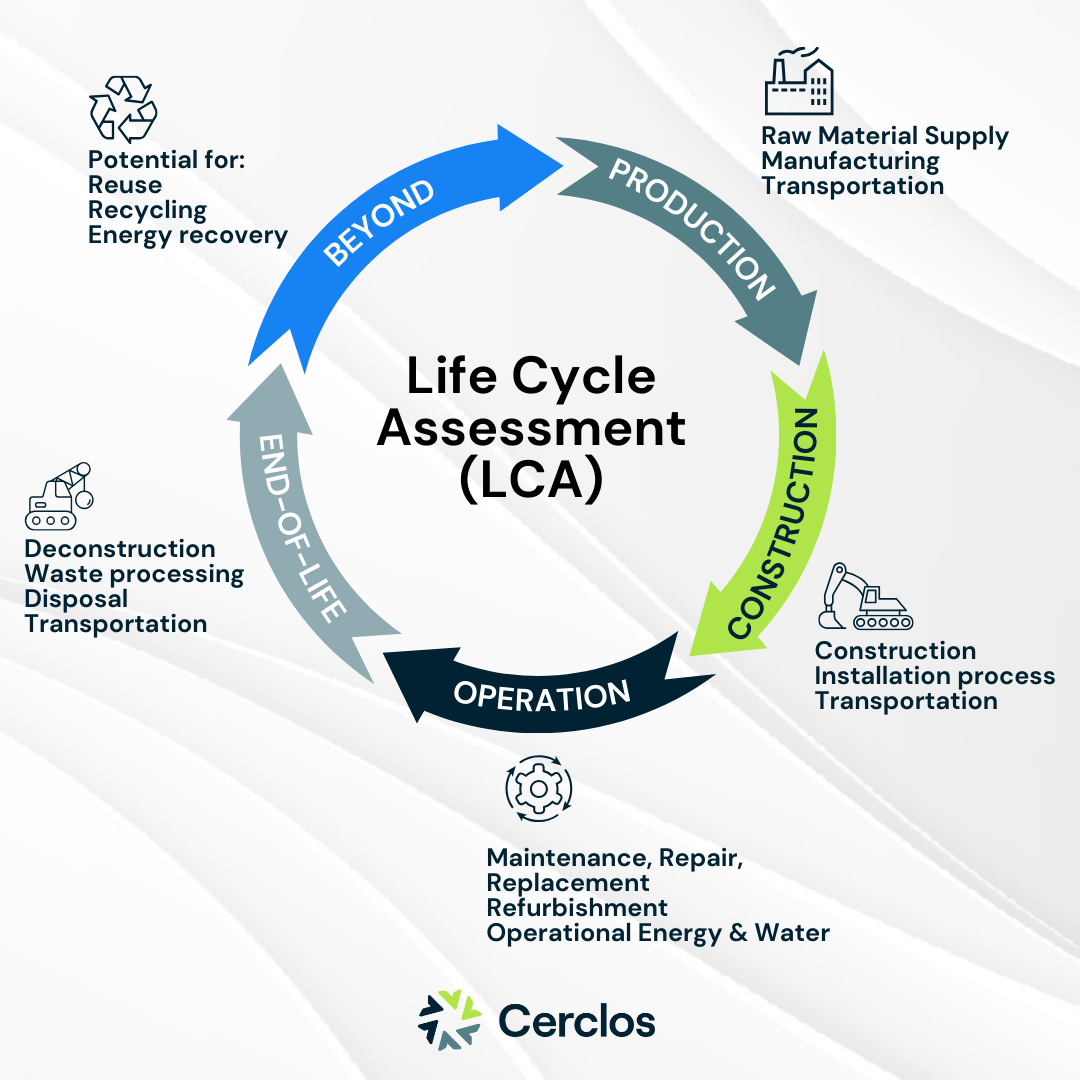
To achieve efficient LCA integration across the mega project, HS2 initiated a tender process to procure suitable LCA tools. Cerclos emerged as the preferred supplier for their flagship software, eTool after rigorous assessment against HS2’s stated functional requirements, such as the system must be compatible with the BS EN 15804 life cycle stages for reporting purposes. Cerclos achieved the highest score across the functional, non-functional and commercial assessments, leading to the award of the contract.
Currently, eTool is adopted by most MWCC Joint Ventures (JVs) and will be used by the rail system contractors upon their onboarding. Station JVs have access to eTool as well, though, they predominantly utilise One Click LCA to maintain consistency with early design phase assessments. A Learning Legacy paper has been published that explores the differences between these two tools[7].
Approach
As the official LCA tool, HS2 and Cerclos have adopted a collaborative approach to facilitate the adoption of eTool across different stakeholders, ensuring consistency, transparency and continuous improvements in integrating its use.
eTool’s core capabilities
Measuring carbon: It calculates and assesses the carbon footprint of the Proposed Scheme, establishing baselines for evaluating reductions during the design, construction, and operation phases for all HS2 assets.
Reducing carbon: Beyond measuring carbon footprints, eTool serves as a valuable design tool that enables users to select less emitting options. Its optioneering feature allows users to iteratively compare different scenarios, enabling the selection of low-carbon options in concept and detailed designs, aiming to minimise embodied carbon in materials, and in detailed construction, utilising innovative and cleaner methods and practices.
Reporting carbon: eTool enables robust and accurate reporting of emissions, ensuring the availability of data for informed decision-making.
Fostering collaboration: The organisation feature allows multiple stakeholders to develop LCA studies together including HS2 internal users and external contractors.
Implementation and support
HS2 prioritised the successful implementation and integration of eTool across their operations and JV network. This involved comprehensive training, and ongoing support facilitated through resources such as eTool Knowledge Hub, community forums and feedback mechanisms provided by Cerclos. Tailored guidance and support articles were also specifically developed by Cerclos to facilitate the set up of HS2 projects, ensuring accessibility for their JVs and streamlining the onboarding process. Regular feedback sessions between HS2 and Cerclos have driven software improvements, enhancing data consistency and usability for complex project requirements. For instance, the bulk import feature was introduced, streamlining the process of importing LCA models in large quantities. This capability minimises data entry time and errors, ensuring greater data consistency, particularly beneficial for a complex project like HS2.
More recently, the Life Cycle Practitioner group was established to further support this collaboration, facilitating quarterly face-to-face interactions among JVs utilising eTool. These sessions enable proactive feedback collection, prompt responses to user queries, updates on Cerclos and eTool software, and deep dives into nominated feature topics shaped by topical issues, support tickets, and forum discussions. HS2 reviews and provides input on these topics, ensuring the presentation content is tailored to their project. A Cerclos LCA expert leads the session, encouraging active participation and feedback on usage recommendations is provided to HS2 post-session. Refer to supporting materials listed below.
Accuracy
The approach involved integrating eTool which has streamlined processes, and automated workflows and ensured overall data integrity and coherence across stages and teams. This lays the groundwork for data consistency, robust analysis, comparability, and data transferability, which are crucial for modelling accuracy and facilitating informed decision-making. At the data level, eTool addresses inconsistency risks in both macro and granular assessments by standardising measurement units and accounting for waste factors that significantly impact results. This approach enables JVs to achieve consistent metric comparisons, conduct accurate LCAs, and standardise reporting.
Baselines and target setting
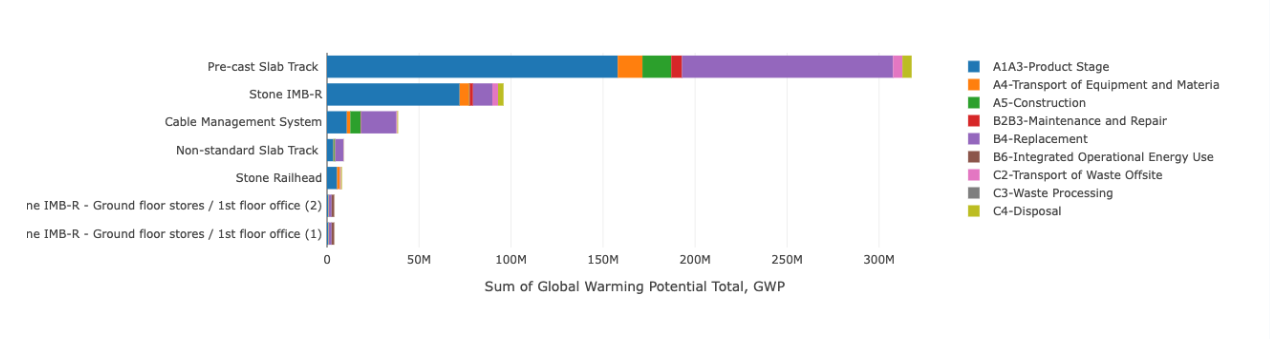
In the early stages, HS2 utilised eTool to establish baselines [Figure 2] for key infrastructure assets, providing a solid foundation for informed decision-making and accountability throughout the project life cycle. Baselines serve as reference points for comparative analysis and demonstrating carbon reduction progress against targets for each contract. This facilitates efficient learning, allowing teams to identify hotspots and make timely decisions. Moreover, the enterprise capabilities of eTool allow different groups to collaborate on creating baseline models and monitor progress towards contractual goals.
For more details on establishing baselines and targets, refer to the paper: Establishing best practice whole-life carbon baselines for Phase One of HS2 – HS2 Learning Legacy[8].
Continuous software improvements
Following the initial implementation of eTool, Cerclos has incorporated HS2 feedback to continuously improve eTool’s functionality, providing users with better insights, and enabling the supply chain to present more compelling business cases for carbon reduction. For instance, the following improvements were introduced:
- Unique Asset ID functionality: Allows users to assign distinct IDs to individual assets within a single project, aligning with the HS2 internal asset ID management system.
- Project Import feature: Allows HS2 JVs to import numerous templates at a project level, significantly improving task execution.
- API integration feature: Allows HS2 to connect eTool with HS2’s building information modelling (or digital twin) for reporting environmental impacts, ensuring integrated data for consistent and repeatable results. This integration was developed through extensive engagement with various key stakeholders such as the HS2 IT team, ensuring that the updated features met the needs of the HS2 user groups.
In essence, this approach relies on collaborative engagements and supportive behaviours from both Cerclos and HS2, to enable successful utilisation of eTool, thereby enhancing the accuracy of results to drive low carbon outcomes.
Project outcomes
Progressing towards targets
The integration of eTool into the HS2 project played a role in achieving significant carbon reduction milestones. In March 2024, the HS2 project reported a 32.5%[9] carbon reduction from the baseline model during Phase One, partly due to eTool’s ability to accurately model and monitor whole-life carbon and guide decision-making towards more sustainable practices.
Low carbon designs
HS2 has achieved significant milestones across its program, with 32 innovative projects projected to save 1.6 million tonnes of carbon emissions[9]. The Interchange station in Solihull has achieved global BREEAM ‘Outstanding’ Certification at the design stage, boasting a remarkable 47.2% carbon reduction against the baseline[9] as of March 2022, placing it in the top 1% of eco-friendly buildings in the UK. Another success story is the Curzon Street Station which achieved a 55% carbon reduction against the baseline[3], attributed to the use of low carbon materials, and energy consumed to operate building integrated systems, such as incorporating solar panels on canopies and Ground Source Heat Pumps.
Lessons learned and recommendations
Training and support for tool adoption
This implementation demonstrated that comprehensive training and support were essential in boosting technical proficiency and confidence among JVs when using LCA tools to meet carbon reduction targets. It also underscored the importance of early tool adoption, where support during setup, thorough understanding of features and processes, clear reporting requirements, and initial training were critical for successful tool implementation.
Recommendation: Ensure LCA tools are complemented with appropriate training resources and user support services to ensure effective tool implementation and efficient achievement of carbon reduction goals.
Collaborative approach for driving continuous improvements
The close collaboration between HS2, the JVs, and the Cerclos team was instrumental in understanding the project’s unique needs and ensuring the successful rollout of eTool across HS2 and its JVs. The experience highlighted the importance of establishing a user group, which Cerclos facilitated, serving as a platform for understanding the eTool software, sharing best practices, resolving issues, and capturing feedback for continuous improvements. These regular interactions led to better transparency, consistency, and data quality, which in turn boosted stakeholder confidence and enhanced the tool’s ability to deliver reliable LCA results.
Recommendation: Create opportunity for LCA tool users (e.g. JVs) and providers (e.g. Cerclos) to directly interact to maximise the efficient and effective use of existing LCA tool functionality and actively seek user feedback to drive continuous improvement aligned with the needs of the user group.
Proper initial project setup ensures seamless integration
Improper setup can cause difficulties in aligning data formats for import into eTool. Ensuring that data is correctly formatted before populating the tool was found to be essential for facilitating seamless and regular data imports.
To address this, it was crucial to configure the project in a way that accommodates the data generated or utilised by the joint ventures (JVs), enabling the extraction of meaningful insights. The HS2 experience demonstrated that insufficient data during the upload stage often limited the depth of insights that could be obtained.
Clear guidelines for the users are essential to ensure that the project is set up correctly, meets all requirements, aligns with eTool processes and enables effective data setup to facilitate smooth integration.
Recommendation: Invest adequate time to support appropriate initial project set up, create controls to manage the set up process and engage the project team to ensure the set up appropriately optimises the needs of the client (e.g. in relation to project portfolio management and reporting) and the specific needs of each project and/or project team.
Integrating eTool with business processes
The HS2 experience highlighted the benefits of integrating eTool into existing business processes to unlock the full potential of the LCA tool. Successfully addressing this challenge required a deep understanding of these processes and how eTool could be aligned to enhance business operations.
Successful implementation of eTool required IT operations to enforce robust security measures, ensure seamless software installations and achieve seamless integrations. To maximise eTool’s utility, it was recommended to partner with HR in developing tailored training programs for employees who rely on the tool. Additionally, working closely with the corporate reporting department helped align carbon reporting and assurance processes, ensuring the full utilisation of all available resources, including third-party certification services like those from Cerclos, to maintain the quality of LCA studies.
Recommendation: Ensure integration and implementation planning looks beyond technology or system integration. People and processes are important and contribute to the overall functioning of the LCA tool. Identify the interplay between people, processes and technologies to effectively balance and coordinate integration with relevant business processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this journey demonstrates the importance of collaboration for effective LCA tool implementation and continuous improvements to advance carbon reduction efforts. Through comprehensive training and integration, stakeholders effectively utilised eTool, contributing significantly to achieving low carbon outcomes across the project. These insights are invaluable for future projects aiming to drive smarter carbon reduction across multiple stakeholders and locations. As sustainability becomes a priority in infrastructure projects, HS2’s holistic approach exemplifies the pivotal role of innovative tools and collaborative strategies in achieving tangible environmental outcomes and operational excellence.
References
[1] Committee on Climate Change (CCC) (2019) Reducing UK emissions: 2019 Progress Report to Parliament. London
[2] HM Treasury (2013) Infrastructure Carbon Review.
[3] Her Majesty’s Government (2019) The Climate Change Act 2008 (2050 Target Amendment) Order 2019 (online).
[4] HS2 Ltd. High Speed Rail (London-West Midlands) Environmental Minimum Requirements. Annex 1: Code of Construction Practice. Birmingham: HS2 Ltd; 2017.
[5] HS2 Ltd. Net Zero Carbon Plan. Birmingham: HS2 Ltd; 2022.
[6] Nrep Decarbonisation policy
[8] Establishing best practice whole-life carbon baselines for Phase One of HS2
[9] HS2 Ltd. Annual Report and Accounts 2023-2024,
[10] HS2 Ltd Environmental Sustainability Progress Reports



