Geotechnics
Geotechnics Resources
Resources include papers, videos, research summaries and good practice documents produced by authors from across the HS2 Family to capture learning, good practice and innovation from the HS2 programme
-
Published on
Saving in lime use for soil stabilisation
Lime stabilisation is used to improve the condition and performance of site won materials to enable their use in earthworks fills. Fills with higher dynamic resilience are required for high-speed rail embankments and foundations. UK specifications have historically set the minimum quicklime addition at 2.5%. With a big drive to reduce carbon and cost on…
-
Published on
Saving in Ground Granulated Blastfurnace Slag (GGBS) and alternative tests for high sulfate mixtures
Swell or heave of lime stabilised high sulfate material has been the cause of numerous high profile construction failures in the last 50 years. The formation of ettringite and thaumasite at temperatures below the standard laboratory temperature 20C (68F)±5C is commonly accepted to be the cause of the swell. The scope of this project involved…
-
Published on
Shaft friction design for piles in extremely weak to weak Mercia Mudstone
There is limited guidance for pile design in the Mercia Mudstone, when it varies between a weathered stiff clay and unweathered weak mudstone. In this transitionary zone, it is common for the mudstone to be found interbedded with varying degrees of weathering over a significant depth, or for the material to gradually transition from a…
-
Published on
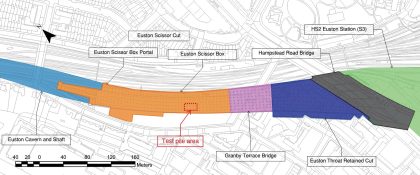
Test pile design, construction and testing – maximising the benefits of preliminary pile test results in pile design and construction at Euston Approaches
A 450m long retained excavation to a maximum depth of 18m close to sensitive 3rd party assets will be constructed to house future HS2 tracks north of Euston station. Approximately 1700 bored piles between 1.2 to 1.8m in diameter, with over 700 located beneath the base slab and founded primarily in the Thanet Sand Formation,…
-
Published on
Colne Valley Viaduct foundation design
The proposed 3.4km long Colne Valley Viaduct provides an excellent opportunity to review and optimise design methodologies for large diameter bored piles within Chalk. Whilst piles have been successfully designed and constructed in chalk for many decades, the HS2 Colne Valley Viaduct will be required to support the highest speeds and dynamic forces of any…
-
Published on
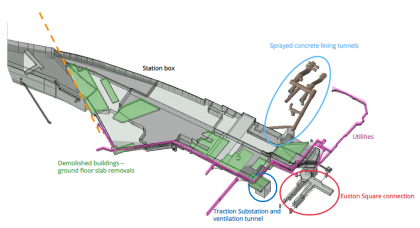
Streamlining utilities ground movement assessments
Ground Movement Assessments (GMAs) involve analysing and mitigating the damage caused by construction related ground movement on strategic utilities, operational tunnels and historically important buildings. Gaining approval from owners of assets located in the densely populated areas around the HS2 Euston Station site, prior to construction works commencing, was therefore integral to the success of…