Environment
An environmental, social and economically integrated approach to development that meets present needs without compromising the environment for future generations.
Topic areas
Environment Resources
Resources include papers, videos, research summaries and good practice documents produced by authors from across the HS2 Family to capture learning, good practice and innovation from the HS2 programme
-
Published on
Pass-by noise assessment of high speed units by means of acoustic measurements in a perimeter close to the train
Characterization of rolling stock from the perspective of exterior noise emission is typically carried out by following the technical procedures detailed in the international standard ISO 3095. Whilst this standard can be considered adequate for conventional rolling stock, the advent of very high speed railway transport has introduced a number of challenges in terms of…
-
Published on
A simplified model for calculating the insertion gain of track support systems using the finite difference method
In the procurement of track support systems for railways planned in the vicinity of receptors sensitive to groundborne noise and vibration it can be necessary to specify parameters of components of the system in order to ensure that its in-service performance will deliver the required level of mitigation against the effects of groundborne noise and…
-
Published on
Embedding circular thinking in a major UK infrastructure project
High Speed Two Limited (HS2 Ltd) has identified that there is a strong alignment between the High Speed Two strategic goals and potential circular economy benefits and has therefore adopted a holistic approach to realising these benefits in the delivery of the UK’s new high-speed rail network. This paper describes the work undertaken to date,…
-
Published on
HS2 railway, UK–route development to the hybrid bill: the environmental statement
The environmental statement (ES) for the first phase of the UK's High Speed Two high-speed railway (London to West Midlands) was submitted with the hybrid bill for the project in November 2013. It described the phase one scheme both during construction and operation, detailed the main alternatives considered and reported the likely significant environmental effects…
-
Published on
Carbon dioxide management in a major UK infrastructure project
High Speed Two, a planned high-speed railway in the UK, could play a key role in reducing national greenhouse gas emissions. The project has adopted whole-life carbon dioxide emissions reduction as a core project value and is using the PAS 2080 specification to implement carbon dioxide management. Effective leadership and governance, metrics, innovation and standards,…
-
Published on
Planning for waste minimisation and resource efficiency in HS2
High Speed 2 (HS2) will be the new backbone of Britain's rail network. Phase 1 will be Europe's biggest construction project, creating 230 km of new railway, and will provide significant challenges in waste management, not least the production of approximately 130 Mt of excavated material. HS2 Ltd has developed an Environmental Policy which includes a commitment…
-
Published on
Broadening our horizons: implementing the Historic Environment Strategy for HS2 Phase One
This paper discusses the implementation of the Historic Environment Research and Delivery Strategy (HERDS) for High Speed Two (HS2) Phase One, London to Birmingham. It discusses the question-led approach to the historic environment programme set out in HERDS and considers approaches to both prospection for archaeological remains and selection for further investigation and mitigation. Challenges…
-
Published on
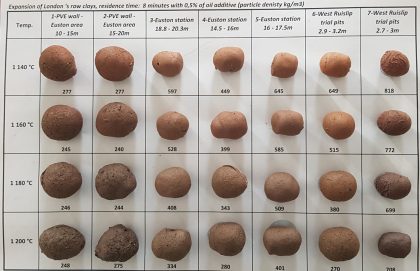
Transformation of London clay into construction resources: Supplementary cementitious material and lightweight aggregate
Resource efficiency, regarding waste minimisation and material re-use, is central to infrastructure construction for both environmental and financial sustainability, especially given the sheer scale of such projects. Maximising resource efficiency can significantly reduce impacts, streamline costs and tackle material scarcity. HS2 will need to manage large amounts of excavation arisings; particularly in Area South, where…
-
Published on
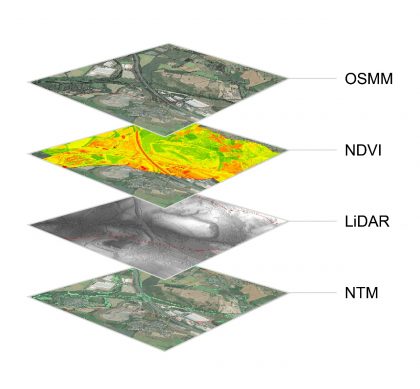
The use of remote sensing to identify habitats on a large-scale linear infrastructure project
The majority of large-scale infrastructure projects are required to undertake an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). This process enables environmental specialists to identify what resources may be impacted by the proposed development in order to influence the design and provide mitigation where required. Part of the process is establishing the pre-existing or baseline conditions. For ecology,…
-
Published on
Use of Sustainability Assessments (BREEAM and CEEQUAL) on the HS2 project
At High Speed Two (HS2), sustainability is all about delivering social, environmental and economic benefits through the ambition of building the most sustainable high-speed railway of its kind in the world. The key sustainability goal is to deliver a railway that respects the natural environment by conserving, replacing or even enhancing wildlife habitats along its…
-
Published on
Powerful forces: electric plant and supply chain collaboration
Supply chain partners who are making the switch to low carbon, high efficiency "clean energy" plant and vehicles have been proactively sought out on the High Speed Two (HS2) Enabling Works Contract (EWC) for Area South. With a huge programme of earth moving and excavation being undertaken in Central London and a global drive towards…
-
Published on
Construction dust: improving industry best practice
A key concern around any construction site is the generation of dust and the short-term nuisance and its long-term health effects. High Speed Two (HS2) aims to avoid emissions associated with the project, but where not possible, has key requirements to ensure these are minimised and reduced through control measures. To ensure the effectiveness of…
-
Published on
Designing and assuring the UK’s largest ever human remains reburial programme
The reburial programme on HS2 Phase One is unprecedented: never has an engineering project been faced with the challenge of such numbers of buried human remains to remove, look after and rebury – over 30,000 people. The legal framework is also new – while the requirements of the High Speed Rail Act mirror those of…
-
Published on
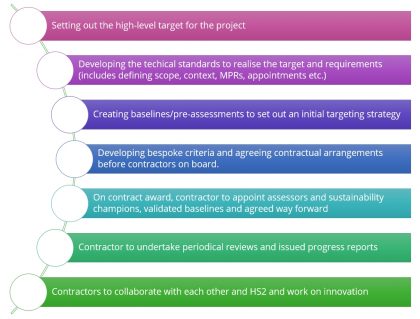
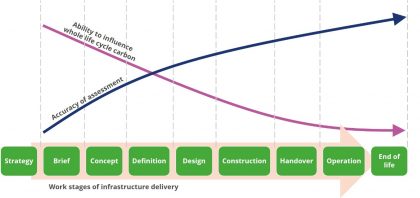
Establishing best practice whole-life carbon baselines for Phase One of HS2
Reducing carbon emissions from infrastructure delivery is key to achieving national carbon emission reductions and is fundamental to addressing the global challenge of climate change. There is also a compelling business case for reducing infrastructure carbon emissions. Reducing carbon emissions can reduce costs, unlock innovation and drive better solutions, drive resource efficiency and deliver better-performing…
-
Published on
Delivering a climate change resilient railway
Resilience is core to being a good business. One of the greatest risks that businesses face is adapting to climate change. HS2 is mitigating climate change by reducing its emissions, including implementing and delivering tough carbon reduction targets. However, even given efforts to limit the cause of global warming, further climatic changes are inevitable in…
-
Published on
Predicting sound levels generated by jet fan ventilation systems in tunnels
The operation of jet fans to ventilate tunnels generates sound that propagates within the tunnels, and can be emitted to external locations, which may include noise-sensitive receptors. To achieve suitable predictions of noise impact, it is important to account for the propagation of sound inside tunnels, which is an engineering problem not addressed by current…
-
Published on
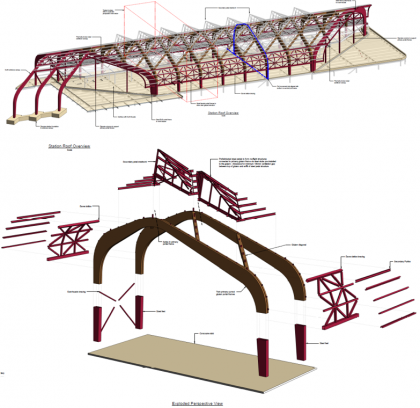
HS2 Interchange Station – Innovative Roof Design: An exemplary project on Integrated Design Team collaboration and the use of advanced Digital Workflows
The design of the roof at Interchange station embodies the HS2 Design Vision. It is both a conceptual response to its site’s rural context and a demonstration of how integrated design can achieve a solution that is visually elegant, cost effective, simple and safe to construct, that minimises both operational and embodied carbon and is…
-
Published on
Minimising carbon emissions at HS2 Phase One Stations
The High Speed Two (HS2) Sustainability Policy sets out the programme’s ambition to build the most sustainable high-speed railway of its kind in the world. The Phase One stations are at the forefront of this ambition and will provide new transport hubs in both Birmingham and London. Phase One stations are tasked with achieving net…