Design, Engineering and Architecture
This theme covers the technical design, engineering and architecture for the HS2 Programme
Topic areas
Design, Engineering and Architecture Resources
Resources include papers, videos, research summaries and good practice documents produced by authors from across the HS2 Family to capture learning, good practice and innovation from the HS2 programme
-
Published on
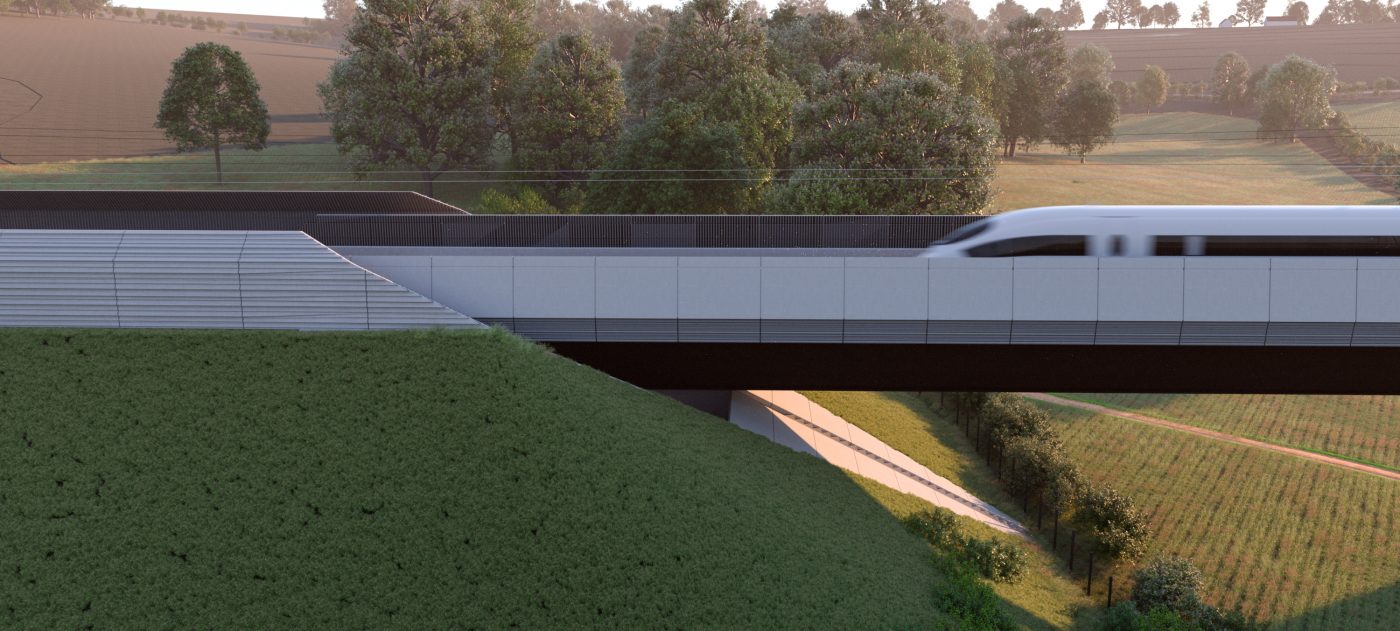
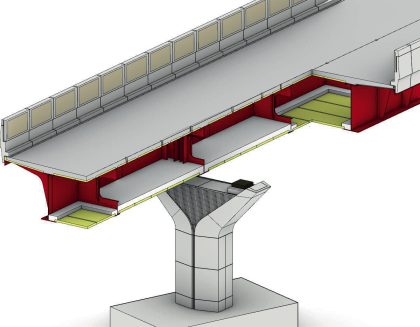
Integral Bridges in HS2
The design of integral bridges may entail significant advantages in some cases as the elimination of bearing devices and structural expansion joints results in a clear improvement of the functionality and safety of the structure in comparison with traditional railway viaducts, while significantly reducing the maintenance liabilities. This is especially relevant when considering the entire…
-
Published on
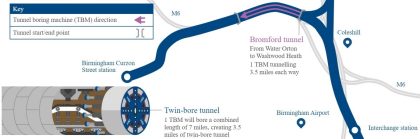
Bromford Tunnel extension – design and environmental benefits with no additional land take
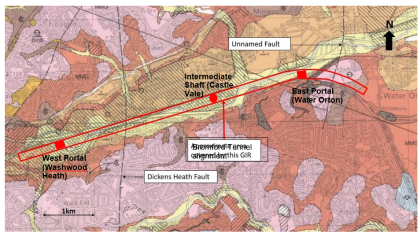
The extension of Bromford tunnel by 3km represents a major design change; how was this achieved without additional land take whilst also bringing wider benefits? Although an extended tunnel reduces the overall surface-level footprint of the High Speed Two (HS2) scheme, the corresponding additional shaft infrastructure, relocated portal and significant changes to construction logistics, bring…
-
Published on
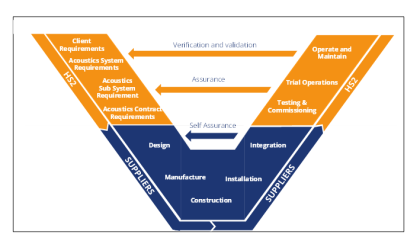
Management of acoustics integration on HS2 for delivering environmental commitments
Environmental noise from the HS2 Railway is the product of the complex interaction of its constituent subsystems (i.e., train, railway systems and civil infrastructure) within the operational parameters of the railway. This paper sets out the approach for delivering the end-state HS2 railway that can operate within the noise limits of the Environmental Minimum Requirements…
-
Published on
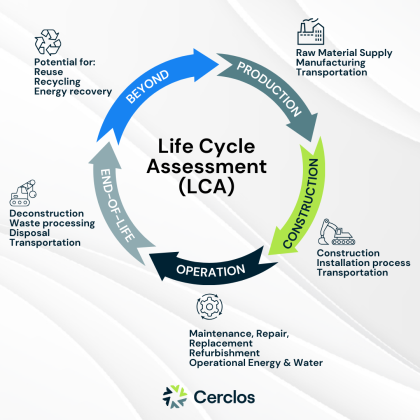
Leveraging Lifetime Cycle Assessment (LCA) for smarter carbon reduction
This article explores HS2’s approach for carbon reduction, emphasising their collaborative partnership with Cerclos in implementing Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology, through the eTool software. HS2 and Cerclos have worked closely to engage stakeholders, improve software to streamline processes and enhance accuracy in LCA results. This strategic partnership offers valuable insights for stakeholders seeking effective…
-
Published on
Saving in lime use for soil stabilisation
Lime stabilisation is used to improve the condition and performance of site won materials to enable their use in earthworks fills. Fills with higher dynamic resilience are required for high-speed rail embankments and foundations. UK specifications have historically set the minimum quicklime addition at 2.5%. With a big drive to reduce carbon and cost on…
-
Published on
Saving in Ground Granulated Blastfurnace Slag (GGBS) and alternative tests for high sulfate mixtures
Swell or heave of lime stabilised high sulfate material has been the cause of numerous high profile construction failures in the last 50 years. The formation of ettringite and thaumasite at temperatures below the standard laboratory temperature 20C (68F)±5C is commonly accepted to be the cause of the swell. The scope of this project involved…
-
Published on
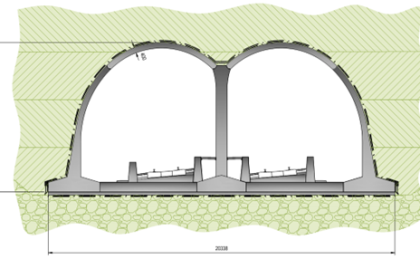
High Speed Rail 2 ( HS2) G2S green tunnels fire design assessment review
This paper presents the design methodology adopted to evaluate the response of a pre-cast reinforced concrete cut-and-cover tunnel subjected to an accidental fire load. The design methodology adopted a simplified fire assessment with an advanced thermal-mechanical numerical analysis completed in parallel. The advanced numerical analysis adopts a transient semi-coupled thermal-mechanical numerical analysis with temperature dependant…
-
Published on
Control of hand and arm vibrations on HS2 and beyond
Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) is a health condition caused by the vibration from any hand-held, fed or guided power tools and machinery on site, e.g. drills, torque wrenches, plate compactors etc. HAVS causes damage to muscles, nerves, joints and blood vessels, leading to permanent long-term health. Over two million people in the utility and…
-
Published on
Re-use of excavated materials
This paper focusses on the sustainable re-use of excavated earthworks materials and the lessons learned as part of the EKFB journey. The objective for EKFB, as the main works contractor for C2 and C3 of the HS2 route, is to maximise the re-use of materials and minimise off-site disposal. This has been achieved through the…
-
Published on
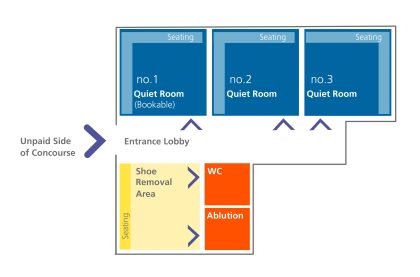
A new standard for health and well-being: HS2 quiet spaces technical specification
HS2 Ltd has strategic goals for setting new standards for customer experience and health and safety in the operation of the railway and therefore requires its designers to take an inclusive design approach so that infrastructure is designed for the people who use it, both customers and staff. Providing quiet spaces for people from religious…
-
Published on
Benefits of steel-concrete bridges with double composite action
The paper aims to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the double composite section in high-speed railway bridges from the design, construction and maintenance point of view. The paper is centred around the differences between single and double composite sections. Steel composite construction has been extensively adopted in the last 60 years for small to…
-
Published on
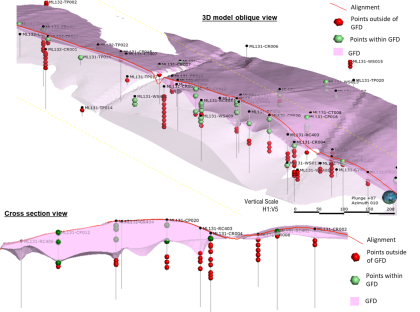
Comparison of predicted versus actual ground settlement during tunnelling
The “Traction Substation package” for HS2 comprises the construction works for the relocation of an existing London Underground Ltd substation on the corner of Drummond Street and Melton Street. The works involved two sprayed concrete lining tunnels, excavated from a construction access shaft, that tie into the existing LUL infrastructure and connect to a piled…
-
Published on
Shaft friction design for piles in extremely weak to weak Mercia Mudstone
There is limited guidance for pile design in the Mercia Mudstone, when it varies between a weathered stiff clay and unweathered weak mudstone. In this transitionary zone, it is common for the mudstone to be found interbedded with varying degrees of weathering over a significant depth, or for the material to gradually transition from a…
-
Published on
The cutting edge (a resilient plant procurement strategy supporting HS2’s Green Corridor)
High Speed Two (HS2) is a catalyst for growth across the UK. Along with this comes not just environmentally responsible landscape and ecological design but, offers a once in a generation opportunity to secure a green corridor that fuses the railway with its contextual landscape. Central to delivering this is HS2’s Plant Procurement Strategy. This…
-
Published on
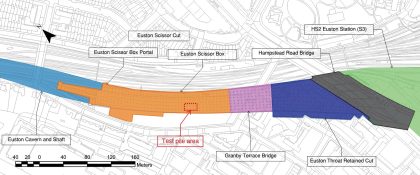
Test pile design, construction and testing – maximising the benefits of preliminary pile test results in pile design and construction at Euston Approaches
A 450m long retained excavation to a maximum depth of 18m close to sensitive 3rd party assets will be constructed to house future HS2 tracks north of Euston station. Approximately 1700 bored piles between 1.2 to 1.8m in diameter, with over 700 located beneath the base slab and founded primarily in the Thanet Sand Formation,…
-
Published on
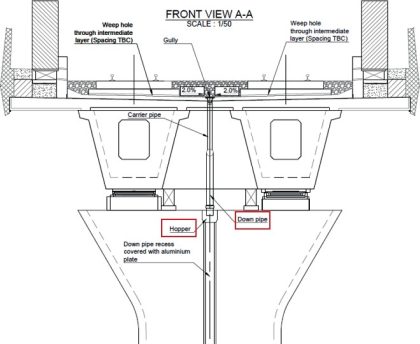
Simplification and automation of design process for HS2 viaducts drainage elements
Viaducts structures are assets adopted in High Speed Two (HS2) to minimise the impact of the railway on the existing motorways, watercourses, and other low-lying developments. The design of surface water drainage systems on high-speed rail viaducts can be a challenge for drainage engineers due to the limited specific research and available design manuals. Yet,…
-
Published on
Railway drainage design in constrained environments. A case study in the vicinity of HS2 Birmingham Interchange Station
The HS2 Birmingham Interchange Station has been located to provide connections to multiple transport modes and routes. It is surrounded by major roads and situated close to Birmingham Airport and the existing Network Rail Birmingham International Station. Given its proximity to new and existing infrastructure, the design of the drainage for the catchment areas around…
-
Published on
The use of measuring-while-drilling to aid investigation of Mercia Mudstone and other weak rocks
The investigation and accurate characterisation of weak rocks can be extremely challenging when fracturing and weathering creates difficulties in sampling and testing from boreholes. One such material is the Mercia Mudstone Group (MMG) that is prevalent along parts of the northern section of High Speed 2 Phase One route. Investigation into the strength and potential…
-
Published on
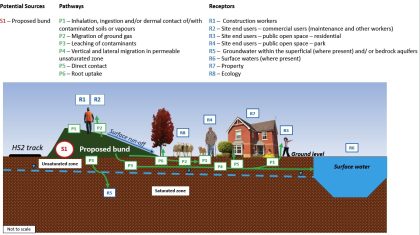
Route-wide contamination risk assessment modelling in support of a sustainable earthwork material reuse framework
High Speed Two (HS2) aims to re-use a minimum of 95% of soils generated by the scheme. This poses challenges for the re-use of potentially contaminated materials. In support of a Material Management Plan for the northern section of the HS2 Phase One works, a contamination risk assessment was produced to derive Acceptability Criteria (ACs)…
-
Published on
Investigation of the behaviour and the design for piles subject to ground heave
The High Speed Two (HS2) mainline crosses deep cuttings in Charmouth Mudstone. Deep excavations cause significant stress changes in the ground which inevitably result in ground heave. However, there is a dearth of research and design guidance currently available for piles subject to ground heave induced by deep excavation in Charmouth Mudstone. In this paper,…
-
Published on
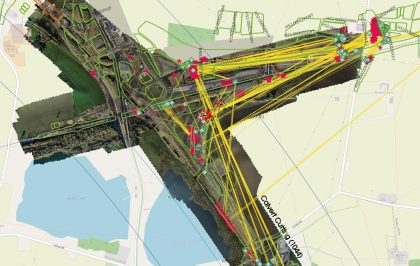
Colne Valley Viaduct foundation design
The proposed 3.4km long Colne Valley Viaduct provides an excellent opportunity to review and optimise design methodologies for large diameter bored piles within Chalk. Whilst piles have been successfully designed and constructed in chalk for many decades, the HS2 Colne Valley Viaduct will be required to support the highest speeds and dynamic forces of any…
-
Published on
Designing with landscape maintenance in mind
The HS2 project is delivering built infrastructure and natural environments on an unparalleled scale. The project affords a once in a generation opportunity to deliver nationally significant infrastructure that will respond to local landscape character and demonstrate an innovative and environmentally-sensitive design approach. The project has been developed to minimise it’s impacts on the surrounding…
-
Published on
Driving efficiency and sustainability in material reuse through GeoBIM
With over 21 million cubic metres of material (equivalent to 8,400 Olympic swimming pools) earmarked to be excavated and moved across the 90 km of the northern section of the High Speed Two (HS2) Phase One route, an accurate understanding of the material types for the re-use of materials in earthworks is a prerequisite for…
-
Published on
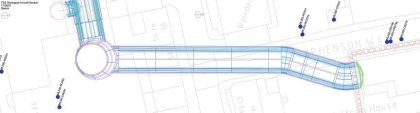
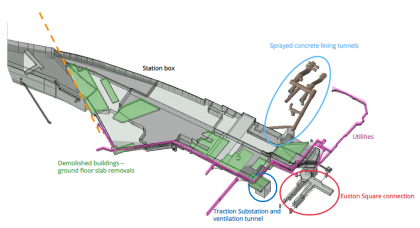
Mitigating the effects of tunnelling under Euston Bridge 7
HS2 tunnels will pass below an existing main line railway intersection bridge near Euston, known as Bridge 7, constructed in the early 20th century. An assessment of tunnelling induced ground movement predicted potential adverse effects on the fragile historic structure. The challenge for the bridge mitigation team was to develop a methodology for logistics, design,…
-
Published on
Streamlining utilities ground movement assessments
Ground Movement Assessments (GMAs) involve analysing and mitigating the damage caused by construction related ground movement on strategic utilities, operational tunnels and historically important buildings. Gaining approval from owners of assets located in the densely populated areas around the HS2 Euston Station site, prior to construction works commencing, was therefore integral to the success of…
-
Published on
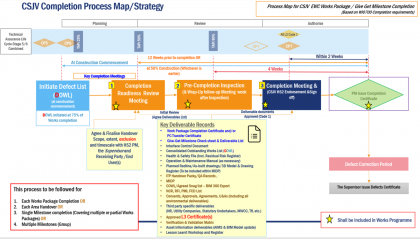
Management of completion and handover
This paper describes the process of planning and managing completion and handover, in particular the importance of starting at the early stage of a contract, defining processes, requirements and deliverables at each life cycle stage, and providing briefings and specific templates for a standardised approach across a complex and diverse programme of works. The increased…
-
Published on
Digitising the permit-to-dig process
Previously, the permit system was aligned to traditional construction sites or rural areas. The team had to adapt certain aspects of the process, to ensure work could be undertaken safely but realistically on mass concrete roads with little spacing between the underground assets. It was also a challenge to get traditional groundworks/demolition packages to work…
-
Published on
Applying temporary works processes to barrier systems
This is the first time that a Utilities contract has had a full temporary works design and inspection regime for our traditional fencing, which is usually Herras. The favoured method used in Euston was water-filled plastic bases with Herras panels clipped in place. There was also a policy in place where acoustic panels were taken…
-
Published on
Improvements for the design and operation of demolition hanging screens and curtains
Following the extensive use of demolition curtains on the Costain Skanska joint venture (CSjv) High Speed Two (HS2) Enabling Works Contract (EWC) South, a guidance document has been produced with the aim of highlighting risk elements, passing on learning and design considerations, and improving the safe system of work employed for this operation. Currently, no…
-
Published on
Reducing the impact of temporary works on third party assets
Costain Skanska joint venture (CSjv) were instructed to undertake the works at the St James Garden (SJG), where the team designed and erected a unique and fully encapsulated mobile scaffold structure to support the archaeological excavation and exhumation works within Area J of the cemetery. To comply with Schedule 20 of the 2017 High Speed…