Digital, Data and Information Management
This theme covers the organisation and digitisation of information about buildings and civil engineering works, including building information modelling
Topic areas
Digital, Data and Information Management Resources
Resources include papers, videos, research summaries and good practice documents produced by authors from across the HS2 Family to capture learning, good practice and innovation from the HS2 programme
-
Published on
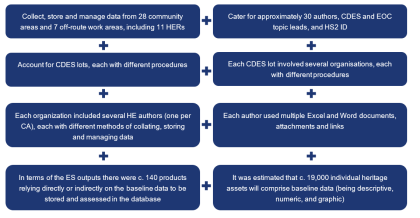
HS2 Phase 2b historic environment heritage asset database
The challenge for the Phase 2b Environmental Statement was to take 1000s of records of heritage assets across the nearly 300km long scheme and try to standardise them so the data could be compared and assessed. This was made more problematic by the fact the records derived from multiple, varied and often contradictory data sources.…
-
Published on
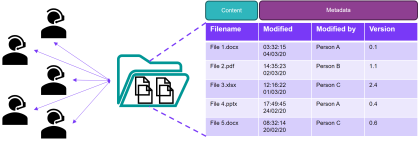
Organising qualitative data into asset databases to standardise reports and improve BIM practices
This report describes the implementation of a data-driven approach to report creation for more efficient, standardised outputs. Vast amounts of information are required to plan, manage, and deliver the High Speed Two (HS2) railway. This information is traditionally delivered in the form of documents or reports. Many of these documents need to be delivered in…
-
Published on
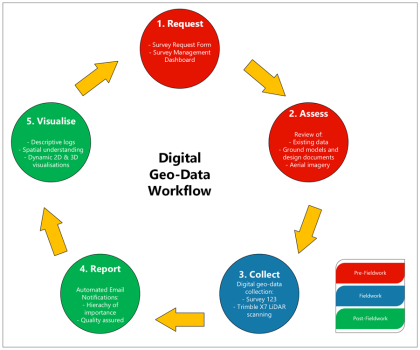
Construction stage geo-data collection, reporting and visualisation – digital workflow
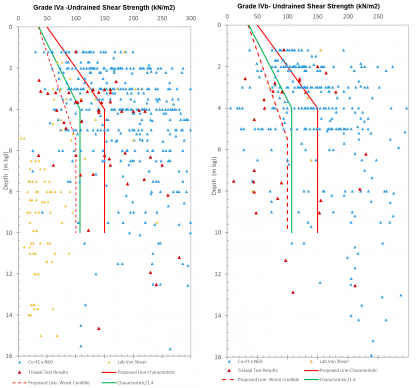
This paper presents an innovative digital workflow designed to address the challenges associated with collecting, reporting, and visualising construction stage geological and geotechnical ground data (geo-data). It emphasises the importance of this data in informed decision-making, to achieve efficiencies, optimisation, and, most importantly, risk assessment and mitigation. The limitations of traditional geological mapping workflows and…
-
Published on
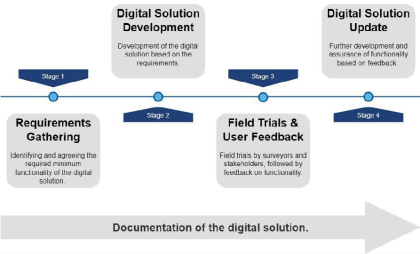
Environmental surveys management – digital innovation
The management and delivery of environmental surveys on a scale as large as High Speed Two (HS2) is an inherently complex challenge. Within HS2 Phase 2a, contractors have been working to deliver 20 different ecology survey types that could potentially be undertaken across over 6,000 land parcels, all with unique rules and constraints. To manage…
-
Published on
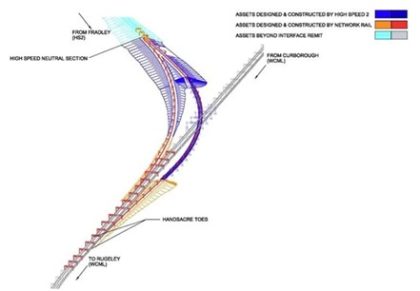
Streamlining design coordination: connecting High Speed Two to the West Coast Mainline
The High-Speed route joins the West Coast Main Line at Handsacre Junction just North of Lichfield, enabling HS2 Phase One services to continue North to Crewe and beyond. All High Speed Two design and construction for assets such as civil structures, track and overhead power is undertaken within the same engineering coordinate system, called the…
-
Published on
Technical process improvement through a systems based approach
This paper focuses on a novel process maturity framework developed during the targeted improvement to the Integrated Design Review and Assurance (IDR&A) Process, by the Skanska Costain STRABAG (SCS) Joint Venture, for the delivery of HS2’s Main Works Civil Contract Southern (the Project). The Project has written processes and procedures for each discipline, with over…
-
Published on
Driving efficiency and sustainability in material reuse through GeoBIM
With over 21 million cubic metres of material (equivalent to 8,400 Olympic swimming pools) earmarked to be excavated and moved across the 90 km of the northern section of the High Speed Two (HS2) Phase One route, an accurate understanding of the material types for the re-use of materials in earthworks is a prerequisite for…
-
Published on
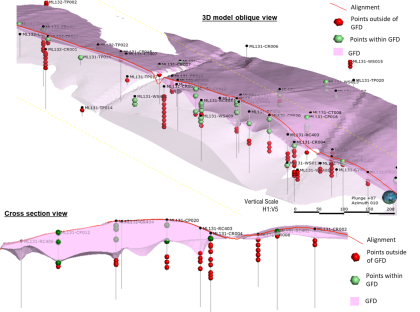
Streamlining utilities ground movement assessments
Ground Movement Assessments (GMAs) involve analysing and mitigating the damage caused by construction related ground movement on strategic utilities, operational tunnels and historically important buildings. Gaining approval from owners of assets located in the densely populated areas around the HS2 Euston Station site, prior to construction works commencing, was therefore integral to the success of…
-
Published on
Leading advances in Level 3 Self Certification
On High Speed Two (HS2), the contractor is responsible for ensuring that the Contract and Works Information requirements are followed. Part of these requirements is to deliver a completely self-assured product throughout the lifecycle stages of the project. The Level 3 (L3) certificate attests that the product delivered to the client is fully assured technically…
-
Published on
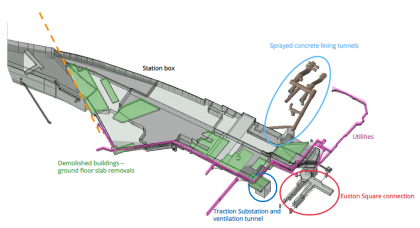
Fully digital and paper-free office
The Euston Power Signal Box (PSB) office utilised an integrated digital system, enabling all site activities to operate under a paperless system with full engagement from the key supply chain partners. The digital system has replaced all paper documentation, improving efficiency, quality and environmental credentials. The PSB digital office has set a new standard for…
-
Published on
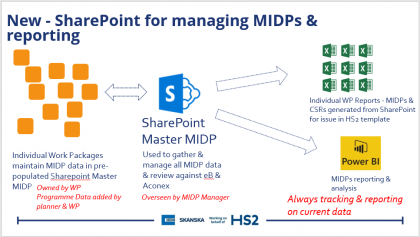
Super MIDP (Master Information Delivery Plan)
Early identification, adoption and system development for the workflow management of deliverables is critical to overall success of a project. Looking forward, the Super Master Information Delivery Plan (MIDP) should be one of the key data sets sitting under the remit of the Project Information Manager (PIM) who will be able to combine the insight…
-
Published on
360-degree trial pit photography
Trial pit photographs captured using conventional digital cameras during ground investigation works are typically of poor quality because of lighting conditions and viewpoint, missing out on key opportunity to capture a photographic record of the in-situ ground conditions. The paper documents the findings of a 360-degree camera photography trial on the Phase 2A ground investigation…
-
Published on
Advances in Engineering Survey Grid Transformations for Rail Infrastructure
This paper provides a summary of innovative approaches developed on Snake Projection coordinate transformations that maximise data interoperability and compatibility within CAD, GIS and survey software and systems. The project’s topographical survey, design and construction use an engineering coordinate system defined by the HS2 Snake Projection together with the HS2 Vertical Reference Frame. This approach…
-
Published on
Using Train-Borne Lidar to improve design confidence in railway electrification
The Midland Main Line needs to be remodelled and electrified to accommodate High Speed Two (HS2) train services to Sheffield. This paper addresses how the issue of site surveys, to accurately judge the level of intervention required for the system design, without site access, was solved. Detailed measurements were required on the 26km route, which…
-
Published on
Automation process for the delivery of Design Element Statement Reports
This paper outlines the development, functionality and benefits of automating delivery of Design Element Reports on the High Speed Two (HS2) Programme, leading to improved efficiency and consistency. A Design Element is an individual, or group of HS2 civil engineering assets that are summarised in Design Element Statements for the purpose of informing the Environmental…
-
Published on
Soils, Landscape and Woodland: How HS2 is using integrated asset information management in a BIM environment.
High Speed Two (HS2) is delivering a new environmental framework alongside the railway infrastructure; creating landscape plantings sites and new ecological habitats and features in advance of the main construction works. Before it comes into operation, Phase One of the HS2 Project intends to create around 650 hectares of new woodlands, to provide new habitats,…
-
Published on
Automation of soil-structure interaction finite element modelling using Python coding and the project BIM model
This paper describes novel methods and tools used to set up, run and review results from multiple 2D finite element analyses for the High Speed Two (HS2) Euston Scissor Cut, using the project BIM model, Plaxis’ remote scripting Python wrapper and PowerBI. By automating a number of manual processes, the design team was able to…
-
Published on
Towards a Digital Blueprint: data, technology and collaboration at the core of HS2
This project is one of the most complex and challenging railway initiatives the United Kingdom has ever undertaken. Tasked with saving the government £500 million in digital efficiencies, HS2 is committed to applying global best practice in design and construction, setting strict data and modelling requirements in accordance with Government BIM (Building Information Modelling) standards.…
-
Published on
Incorporation of digital ground investigation data and geological model into the 3D BIM environment
Traditionally, geological interpretation is undertaken by manually annotating cross-sections, and updating them when new information becomes available. This is a time-consuming process and goes against the principles of good digital engineering. A workflow was developed for High Speed Two (HS2) so that raw ground investigation information forms a database that is then used to generate…
-
Published on
Infraworks models to assist with construction sequencing and planning
Autodesk Software package InfraWorks is a 3D Infrastructure planning and design tool which is being used to model specific areas of the High Speed Two (HS2) proposed route and the proposed construction sequences respectively. This paper focuses on the creation of the models, data processing, material volume reports and the benefits that these models have…
-
Published on
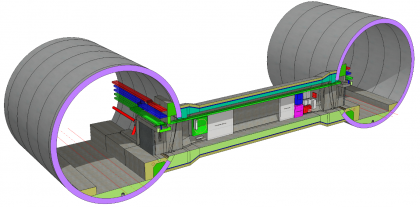
Using 3D models and BIM for the Chiltern Tunnel Design
Building Information Modelling (BIM) has been adopted for the design and build of the 16km Chiltern TBM Tunnel as part of the High Speed Two (HS2) project. A complete set of 3D structure models including two portals, two bored tunnels, five intermediate shafts and 40 cross passages is a key deliverable to HS2, as it…
-
Published on
Digital mapping of environmental significant effects on HS2 Phase 2a
Protected species constraints are an early consideration for nearly every development project, and where impacts cannot be avoided mitigation licensing is a legal requirement. HS2 Ltd are the licensee for a great crested newt organisational licence, as part of the Phase One works; the largest such licence ever issued by the regulator for a single…
-
Published on
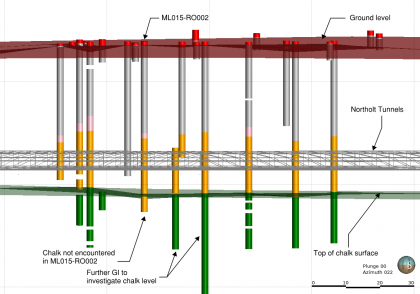
Innovative ground data management
Engineering geologists and geotechnical engineers need the right tools to efficiently investigate, analyse, model and share their geological understanding of expected ground conditions with the wider project team as and when new data becomes available. National large-scale infrastructure projects like High Speed Two (HS2) provide significant technical ground and engineering design challenges but they are…
-
Published on
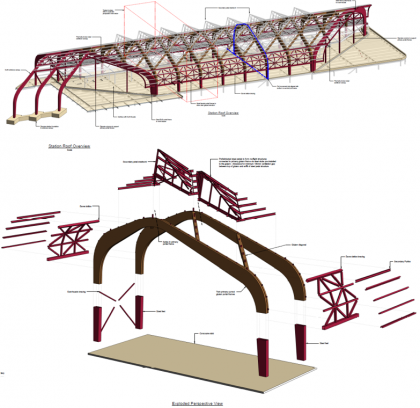
HS2 Interchange Station – Innovative Roof Design: An exemplary project on Integrated Design Team collaboration and the use of advanced Digital Workflows
The design of the roof at Interchange station embodies the HS2 Design Vision. It is both a conceptual response to its site’s rural context and a demonstration of how integrated design can achieve a solution that is visually elegant, cost effective, simple and safe to construct, that minimises both operational and embodied carbon and is…
-
Published on
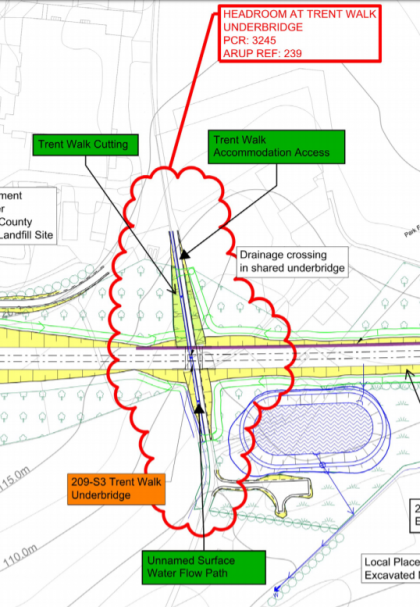
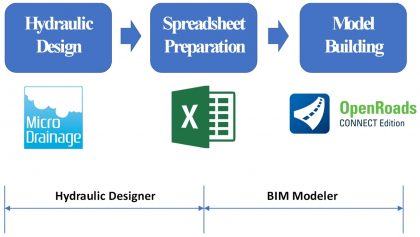
Bridging the gap between drainage design and BIM modelling
The design of the civil engineering works in High Speed Two (HS2) is a good example of what can be achieved when the Building Information Modelling (BIM) process is embraced. Central to the BIM process is a three-dimensional (3D) model that communicates the civil design to enable construction, asset management, operation and maintenance in a…
-
Published on
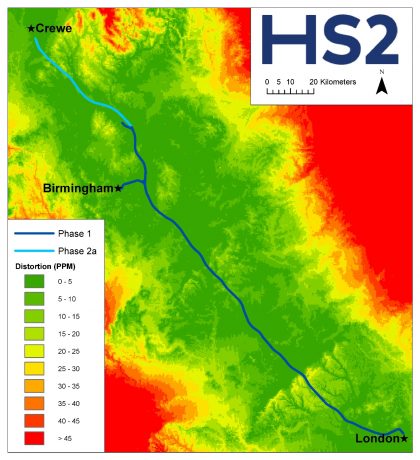
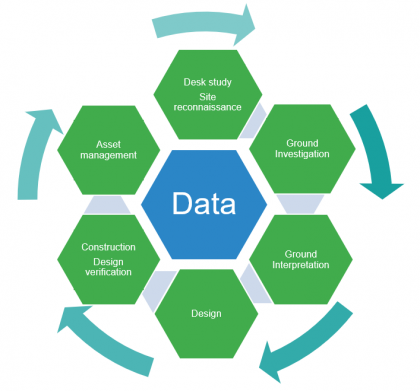
Managing uncertainty in ground conditions in design on a megaproject where ground investigation is highly variable
Ground conditions present one of the major areas of uncertainty and risk for High Speed Two (HS2) Phase One and have a significant impact on project affordability. The ability to effectively and appropriately manage ground risk in design in a consistent manner is complicated by the varying degrees of completeness of ground investigation which may…